PCOS and Fertility: Everything You Need to Know
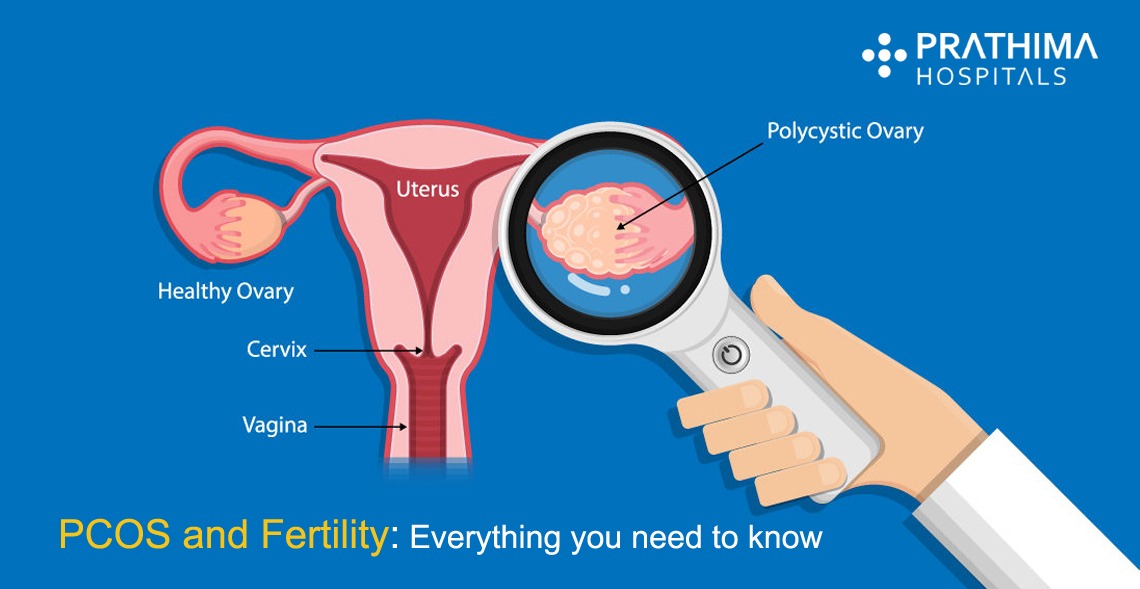
A common endocrine disorder causing disruption in ovulation and menstrual cycles, as well as an excess production of male-type hormones, is a major cause of fertility problems. The cause of which remains complex, a combination of genetic and environmental factors could be a major possible cause of PCOS.
A range of symptoms, including acne, obesity, hirsutism (male-type hair growth of face), oligomenorrhea (few periods), insulin resistance, and enlarged multi-cystic ovaries, etc can be seen in women with PCOS.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome, is a condition related to hormones in which the ovaries are unable to release an egg at the end of the menstrual cycle (the start of a period to the start of the next one). This can lead to fertility problems and trouble in conceiving.
If a woman does have polycystic ovaries (PCOS):
- The ovaries are slightly larger than normal
- They have many more follicles (the fluid-filled pockets on the ovaries that release the eggs when ovulating)
Having polycystic ovaries does not mean that you have PCOS. PCO means your ovaries are slightly varying from most women’s ovaries, while PCOS is disorder linked to having imbalanced hormone levels.
Symptoms of PCOS:
Having PCOS does not necessarily mean that you have PCOS.
To be diagnosed as having PCOS you would have PCOS and some of the following symptoms:
- irregular periods or none,
- PMS or pelvic pain
- acne or oily skin,
- hirsutism (excessive hair growth in areas on the face, neck, chest, stomach, back, hands, feet),
- oligomenorrhea (few periods),
- excessive facial or body hair,
- balding/thinning of hair,
- difficulty losing weight or rapid weight gain,
- difficulty in getting pregnant,
- recurrent miscarriages,
- insulin resistance or Type 2 Diabetes,
- enlarged multi- ovarian cysts,
- Skin tags
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure, etc.
More about PCOS:
- Women with PCOS have slightly higher than normal levels of testosterone – this is linked to many of the symptoms, such as acne or excessive facial/body hair.
- If you have PCOS, your body may not respond to insulin (this is known as insulin resistance), so the level of glucose is higher in your body. High levels of insulin can lead to weight gain and fertility problems. If you are diagnosed with PCOS, you are at increased risk of developing diabetes in later life too.
Causes of PCOS:
There could be various underlying causes of PCOS:
- Genes
- Inflammation
- Insulin resistance
- Defect in pituitary glands
- Certain external/environmental factors
- Other unknown underlying causes
Treatment Options for PCOS:
The following treatment options are available to restore regular ovulation and menstrual cycles in women with PCOS and other menstrual irregularities.
Customized treatment plans are developed after a detailed medical history and evaluation
- Weight management – For obese and overweight women with PCOS, weight loss can restore ovulation and reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Healthy diet – Maintaining a balanced and healthy routine of food consumption.
- Medications –
Clomiphene citrate (clomid) is a medication that causes an increase in production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which promotes development of a mature follicle and ovulation.
Aromatase inhibitors are another class of drugs that may induce ovulation. If patients do not ovulate with clomid, it is unlikely that an aromatase inhibitor will help.
Certain forms of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Homone) can be administered via a subcutaneous injection to induce ovulation. This type of medication must be monitored with blood work and ultrasound to prevent over-response of ovaries, which is a high risk for women with PCOS
- Laparoscopic surgery – Ovarian diathermy is a minimally invasive surgical treatment that can trigger ovulation. This procedure has the benefit of promoting single egg ovulation, thus reducing the risk of multiple conceptions. The drawbacks include the short- and long-term risks of surgery.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) – In vitro fertilization involves combining egg cells with sperm cells in a laboratory, rather than in the body. Once fertilization occurs, the embryos are transferred into the women’s uterus, helping achieve pregnancy that will be carried to term and delivered normally.
Several different medications may be given to encourage the production of multiple eggs. Benefits of IVF include an increased pregnancy rate and lower risk of a multiple pregnancy. Drawbacks include increased risk of fetal defects, as well as the invasive nature of the procedure.
Further, young women with PCOS are at increased risk for ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome (OHS).
In summary, the diagnosis and management of PCOS can be complex, but many treatment options exist. From an infertility perspective, PCOS is frequently successfully treated and thus has a truly positive prognosis.
Chances of Conception with PCOS:
Although it is difficult to give statistics as cases vary among women so much and different treatments have different success rates, most women with PCOS will be able to conceive with fertility treatment(s).
We at Prathima Hospitals put in every effort to make your dream come true and achieve a successful pregnancy.
PCOS and Mental Health:
Getting to know that you are having fertility issues can generate various negative feelings, specifically: guilt, anger and failure, which are most commonly seen. However, if you can, think of it as a medical problem that is treatable alongside most other conditions, and not a reflection on you as a couple. Many couples face issues of infertility, and use fertility treatments to conceive. The inconvenient and bitter past is long forgotten in later years after successful conception.
We at Prathima Hospitals try to support our clients as much as we can through our consultations, treatments and expert counseling services. Book an appointment with us today.






Warning: Undefined variable $req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 294
Warning: Undefined variable $commenter in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 295
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 295
Warning: Undefined variable $aria_req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 295
Warning: Undefined variable $req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 298
Warning: Undefined variable $commenter in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 299
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 299
Warning: Undefined variable $aria_req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 300
Warning: Undefined variable $commenter in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 303
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 303