PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
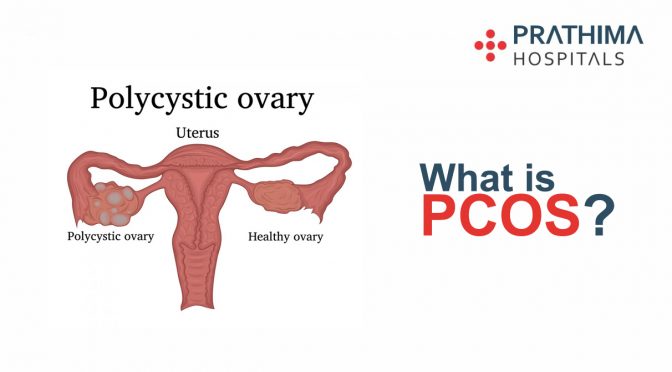
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), also known previously as polycystic ovary disease (PCOD), is one of the commonest endocrine disorders in women belonging to the reproductive age group. It is a condition wherein the ovary starts producing increased amounts of the male hormone testosterone in a female. As a result of this most women present with complaints of irregularity in periods, infertility or excess facial hair and acne. On laboratory testing, most of the PCOS patients have increased levels of testosterone in their blood. On ultrasound, a typical polycystic appearance of the ovaries is seen.
Obesity is the commonest predisposing factor for PCOS. Obesity leads to insulin resistance and increased insulin levels which can predispose a women to develop PCOS. Other common factors which can lead to PCOS are thyroid disorders, diabetes, increased prolactin levels, intake of certain drugs, stress, sedentary lifestyle and poor sleeping habits. PCOS is also hereditary which suggests that certain genes may predispose you for PCOS. Having PCOS puts you at a greater risk for developing diabetes, especially during pregnancy. Other complications of PCOS include miscarriages, uterine cancer, depression, cholesterol disorders, hypertension and fatty liver.
The most important modality of PCOS management is diet and lifestyle modification with emphasis on weight loss. In most cases weight loss can restore fertility with some sub-fertile patients requiring additional medications for ovulatory dysfunction. Furthermore weight loss also reverses the other obesity associated complications of PCOS. Metformin, which is primarily an anti diabetic drug, is effective in decreasing insulin resistance and helps in subsequent fertility.
Oral contraceptive pills are effective in normalising menstrual patterns and decreasing facial hair. Anti androgens are given if the clinical features of increased testosterone, such as increased facial hair and acne, are predominant. Anti androgens should generally be given along with oral contraceptive pills since they can be harmful to foetus if patient becomes pregnant.
Some of the conditions which mimic PCOS include ovarian tumours, adrenal tumours and conditions associated with increased adrenal gland production of male hormones, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia and Cushing syndrome. Consult your endocrinologist for appropriate evaluation since they are all treatable conditions.






Warning: Undefined variable $req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 294
Warning: Undefined variable $commenter in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 295
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 295
Warning: Undefined variable $aria_req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 295
Warning: Undefined variable $req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 298
Warning: Undefined variable $commenter in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 299
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 299
Warning: Undefined variable $aria_req in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 300
Warning: Undefined variable $commenter in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 303
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/u885608126/domains/prathimahospitals.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/prathimahospitals/functions.php on line 303